How To Test Idle Air Control Valve With Multimeter
The idle air control (IAC) valve or motor is one of the most important electrical components within fuel-injected engines.
It is an electrical unit mounted on the body of the throttle that controls the engine air supply to ensure proper combustion during engine idling and even when you speed up.
As expected, when this component develops a fault, the engine suffers and your vehicle performs poorly.
However, a lot of people don’t know how to diagnose it for faults. Not to worry, our article presents you with all you need to know about testing the IAC valve.
Let’s get right into it.

Symptoms Of A Bad Idle Air Control Valve
A good idle air control valve or motor is expected to give an idle between 500 RPM and 1000 RPM, with this displayed on the tachometer on your vehicle dashboard.
This is the average RPM range for most vehicles to keep the engine running while idle.
The RPM also increases when you speed up the vehicle and could go as high as 6000 RPM depending on the speed.
If the idle air control valve motor is bad, however, you experience symptoms like
- Smooth idling outside this recommended idling range,
- Rough idling that erratically goes above and below this idle range,
- Occasional or repeated stalling after engine ignition, or/and
- Illuminated check engine light on the dashboard
It is important to note that the recommended idle range depends on your specific engine model and it may safely go higher or lower.
Refer to your car service manual for the right specifications for when it is idle and when you speed up.
If you experience any of these symptoms, then you know that you need to test the idle air control valve for faults.
Tools Required
To diagnose an idle air control valve for issues, you need a
- Multimeter
- Voltage test light
- OBD scanner/bidirectional scanner
- Car engine service manual
The multimeter is the most important electrical diagnosis tool here.
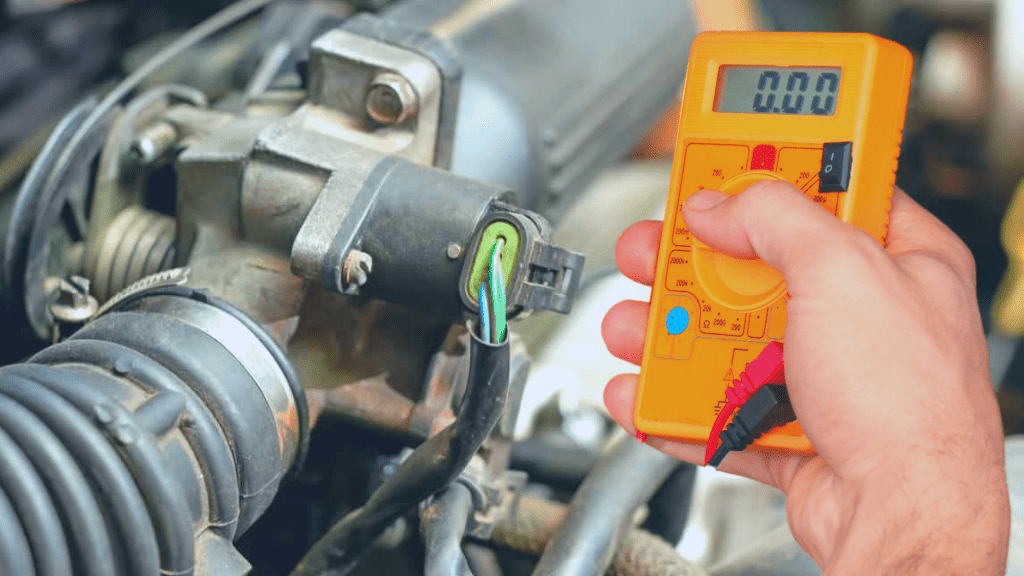
How To Test Idle Air Control Valve With Multimeter
Set the multimeter to measure Ohms, place the red lead on one terminal of the idle air control valve solenoid, and place the black lead on the other terminal. If the IAC valve is in good condition, you get a resistance between 7 and 25 Ohms, depending on its model. Another value means the unit is bad.
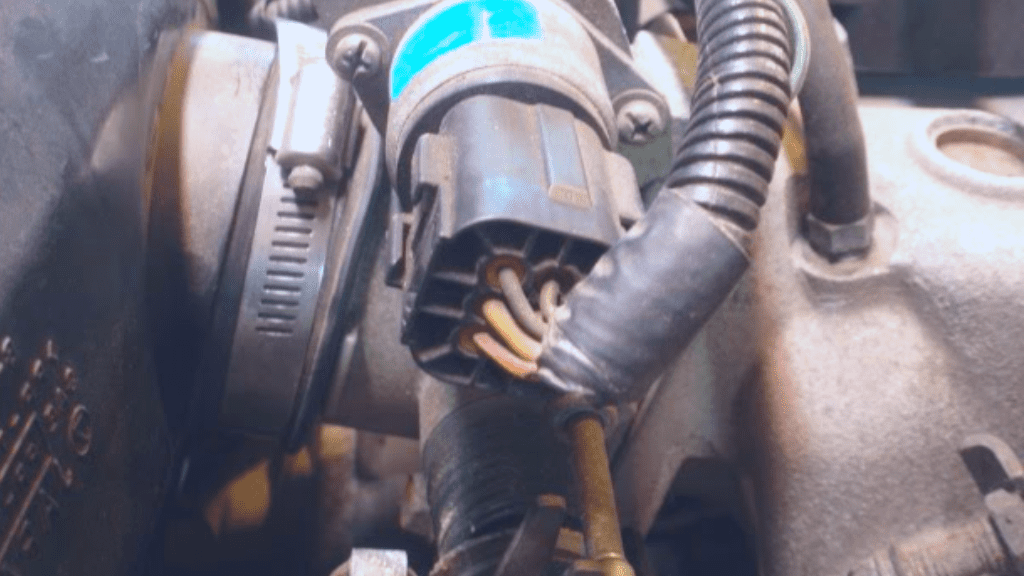
- Locate The Idle Air Control Valve And Take It Out
You want to refer to your car engine manual to pinpoint the exact location of your idle air control valve, as well as how to remove it from the engine.
The IAC is usually mounted on the body of your throttle. It is also connected to the engine through a solenoid mounted on it, so you are typically just required to disconnect the connector from this solenoid.
- Visually Inspect Idle Air Control Valve
Before we pick up the multimeter, we check the IAC valve and other air vacuum components for any physical impurities.
Inspect the IAC sensor for dirt and also check out all vacuum lines for any air leak.
An air leak in your vacuum lines hinders the IAC from properly performing its function. If you notice dirt on the IAC, use an electronics part cleaner to cleanse the unit.
Mount it back on the body of the throttle and see if it works properly. If you didn’t find any issue here, move to the next step.
- Test The Connector For Power
Now, you want to check whether the IAC valve is receiving power (or signal) from the ECU. You need a test light for this.
Depending on how your test light works, place its tip on each of the terminals in the connector circuit.
If you don’t get a light or beep from your test device, then there is a problem with the connector or ECU and not the idle air control valve.
You may also use a multimeter for this by setting it to the 20VDC range, grounding the black probe on a metal surface, and testing each connector circuit for voltage.
If you don’t get a reading between 1V and 12V, the power or signal supply to the IAC valve is bad.
If you got a good indication from any test device, however, then proceed to the main multimeter test.
- Set Multimeter To Measure Resistance
Resistance is represented by ohms on the multimeter, so you put the meter in the ohm setting represented by the omega symbol (Ω).
- Place Multimeter Leads On IAC valve Solenoid Terminals
Now, you place the black negative multimeter lead on one of the idle air control valve’s solenoid terminal and place the red positive lead on the other solenoid terminal.
- Check Resistance Reading
Different IAC valves have different specifications for resistance, and these specifications change whether the IAC is hot or cold.
If the idle air control valve is hot (50°C to 100°C), you expect a resistance value between 21.5 Ohms to 29.5 Ohms.
A cold IAC (-13°C to 50°C) is expected to have a resistance between 17 Ohms and 25 Ohms. In some car models, the resistance value goes as low as 7 Ohms.
Look at the reading presented to you by the multimeter and see if it falls within any of these ranges. If it doesn’t, then the idle air control valve is bad and should be replaced.
Testing Using Idle RPM
Another way to test the idle air control valve is to diagnose a problem by studying how your vehicle idles.

Here, you compare how the vehicle idles when the IAC valve is connected to the engine against when it is disconnected.
- Turn On The Car Engine And Measure The RPM
The first step is to switch on your car engine, check your tachometer, and wait for the idle RPM to get stable.
It may take a few minutes to do this, but once it levels out, you record the stable idle RPM on a sheet of paper.
If the idle RPM never gets stable, then there is a problem with the idle air control valve. If it got stable, however, move to the next step.
- Turn Off The Car And Take Out The IAC valve
After recording the RPM with the IAC valve still connected to the vehicle, you want to remove it from the throttle and take another measurement.
Switch off your car engine and locate the idle air control valve within your vehicle. Referring to your car manual makes this easier. Regardless of this, IAC valves are typically mounted on the body of your vehicle’s throttle.
You then disconnect the connector going to the idle air control solenoid and remove the IAC valve from the throttle or where it is in your vehicle.
The procedure for taking out the IAC valve differs by vehicle model, so your car engine manual is also important here.
- Restart The Car Engine And Take Another Measurement
Now, you turn your vehicle back on and measure the idle RPM for when the IAC valve isn’t connected to it. Don’t worry, your vehicle still works without the idle air control valve, but is expected to have a different idle RPM.
Remember, you turn the engine on, wait a few minutes for the idle RPM to get stable, then record this stable idle RPM on a sheet of paper.
- Check For Differences
If the idle air control valve was working, you’d expect the RPM from these two measurements to be different. This means that the idle air control valve was maintaining control of the RPM while it was in the engine.
However, if your measurements are the same, then the idle air control valve was not performing its function within the engine. This could either be caused by the idle air control valve itself or a bad signal from the engine control unit (ECU).
Diagnosing Using Scan Tools
You may also use diagnostic scan tools like OBD scanners and bidirectional scanners to find problems with your idle air control valve.
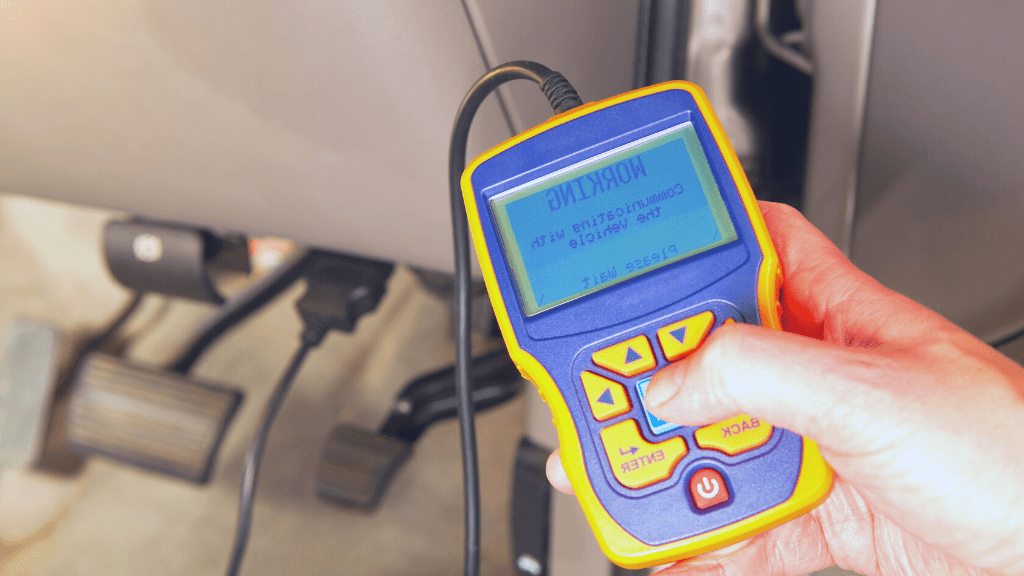

For the OBD code scanner, plug it into the OBD port beneath your car dashboard. An OBD I scanner is appropriate for cars developed before 1996, while an OBD II scanner is for cars developed after 1996.
Check out the diagnostic code presented to you by the scanner. If you get a P0505 error code, for instance, the voltage supplied to your IAC valve motor terminals or circuits is bad.
You may check out this full guide on OBD scanners for more diagnostic codes.
A bidirectional scanner, on the other hand, lets you test out the idle air control valve by boycotting the ECU.
You plug it into the same OBD port under the dashboard and send the appropriate signal to the idle air control valve to increase idle RPM.
If idle increases, you know your problem is with the ECU itself.
However, if it doesn’t, the problem is either from the idle air control valve or the connector circuits at the IAC valve solenoid.
Conclusion
Diagnosing the idle air control valve in your engine for faults is a step by step process you want to follow carefully.
You run a series of easy tests before measuring its internal resistance using a multimeter.The step involving the multimeter presents you with the most accurate result.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens If You Unplug Idle Air Control Valve?
When you remove a good idle air control valve from the engine, the engine stalls when it is idling. This is because, without an IAC valve, the engine gets poor air supply and can’t keep running when idle.
What Is The Voltage Of Idle Air Control Valve?
The expected voltage of an idle air control valve is determined by your car’s battery capacity. If you use a 12-volt battery, you expect your IAC valve to work with a signal between 1V and 12V.

Author
Alex Klein is an electrical engineer with more than 15 years of expertise. He is the host of the Electro University YouTube channel, which has thousands of subscribers.
