Transistor vs Resistor: What’s the Difference?
In the vast realm of electronics, transistors and resistors stand as two of the most fundamental components. Despite their ubiquity, many still need help with distinguishing between the two.
This article highlights their differences, functions, and significance in electronics.
What is a Transistor?
A transistor, in its essence, is a semiconductor device pivotal for amplifying or switching electronic signals. Its historical roots trace back to Bell Laboratories, with William Shockley being one of its key inventors.
Predominantly crafted from materials like germanium and silicon, transistors have become indispensable to modern electronic devices, from radios and computers to cell phones.
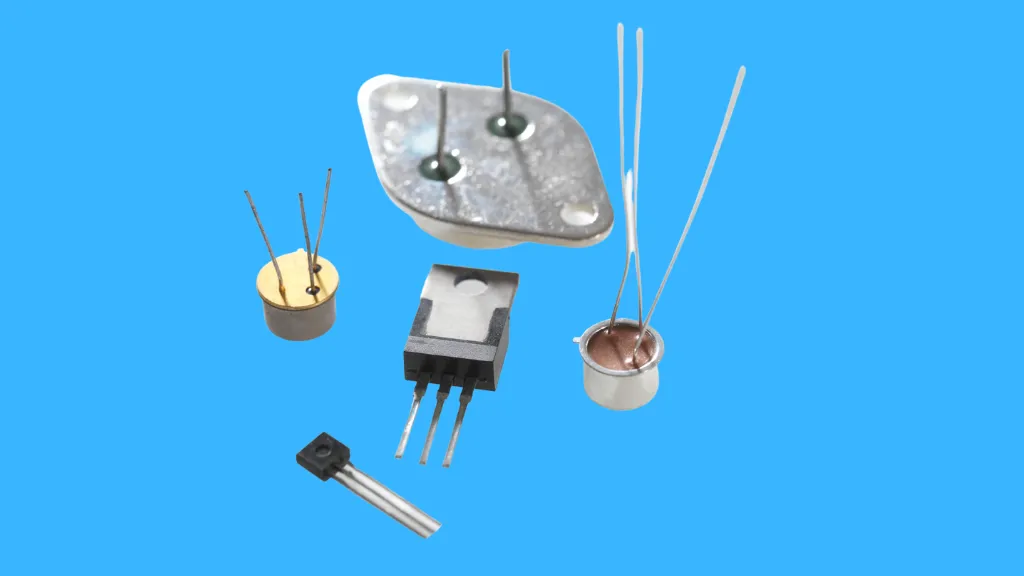
Types of Transistors
Transistors primarily fall into two categories:
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): These come in NPN and PNP variants.
- Field-Effect Transistors (FET): These are further classified into n-channel and p-channel types.
The core distinction between BJTs and FETs lies in their operational mechanisms.
How Transistors Work
A transistor comprises three terminals: the base, collector, and emitter. Its operation hinges on a three-layer system, allowing it to amplify or switch signals based on the current or voltage.
Applications of Transistors
Transistors excel in two primary domains:
- Amplification: They can function as linear amplifiers or switches.
- Switching: Their rapid on/off capabilities are ideal for high-speed operations.
What is a Resistor?
At its core, a resistor is an electrical component designed to regulate the current flow in a circuit. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring that electronic circuits function optimally.
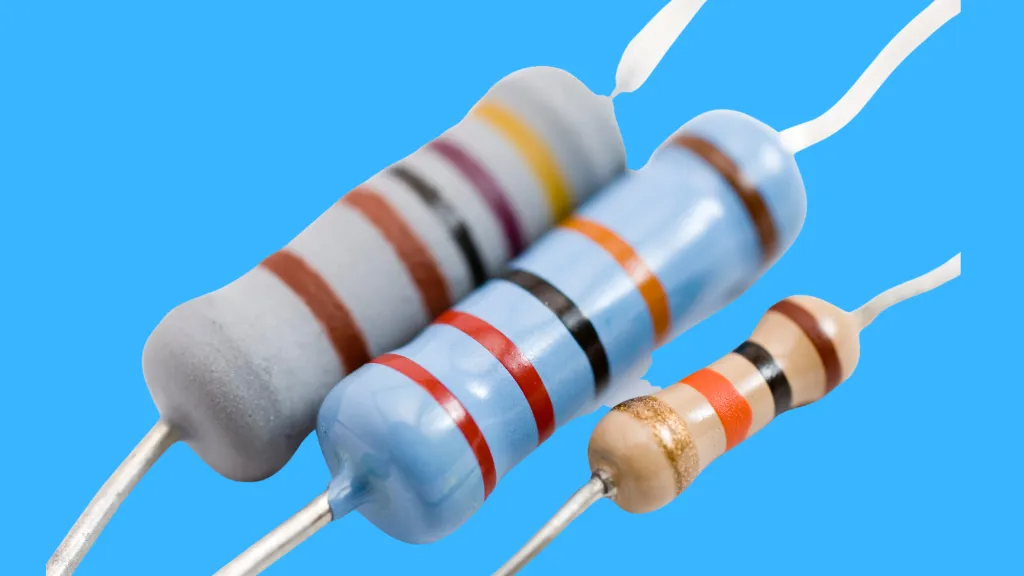
How Resistors Work
The resistance offered by a resistor, measured in ohms, determines the current flow through it. Various materials, including carbon composition, metal film, and metal oxide, are used to manufacture resistors.
Ohm’s law governs the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a resistor.
Types of Resistors
Resistors can be broadly categorized into:
- Fixed resistors: The carbon-film resistor is a popular type in this category.
- Variable resistors: This category includes potentiometers, rheostats, and trimpots, each with unique properties and applications.
Key Differences Between Transistors and Resistors
- Device Type: Transistors are active devices capable of amplifying signals, whereas resistors are passive devices that only offer resistance.
- Working Principle: Transistors can control the flow of electricity, amplifying or switching electronic signals. In contrast, resistors resist the flow of current.
- Usage: Transistors are typically employed to control electrical signals, while resistors are used to limit current.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances between transistors and resistors is crucial for anyone delving into electronics, whether a novice or a seasoned professional. While both are fundamental, they serve distinct roles in ensuring the smooth operation of electronic circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a resistor replace a transistor or vice versa?
No, their functions in a circuit are distinct and not interchangeable.
What is the difference between a transistor, resistor, and capacitor?
While transistors amplify or switch signals, resistors control current, and capacitors store potential energy.
DO I ALWAYS NEED TO USE A RESISTOR AND A TRANSISTOR TOGETHER?
Not necessarily. Their usage depends on the specific requirements of the circuit.
Does a transistor have resistance?
Yes, but its resistance can be modulated based on the current flowing through it.

Author
Alex Klein is an electrical engineer with more than 15 years of expertise. He is the host of the Electro University YouTube channel, which has thousands of subscribers.
