What is a relay, its function, types and relay wiring
A relay is an electrical component that can control the flow of electricity in a circuit. The relay can be energized at one time and de-energized at another. This allows the relay to open and close and interrupt and reestablish electric circuits.
This blog post shows you the most important things you need to know about relays. So if you’re curious about relays, keep reading!
What is a relay used for?
A relay can be utilized in many different types of products. For example, the starter on a car has several relays that control things such as the fuel pump and ignition coils.
They are also very common in household appliances such as your toaster or refrigerator.
In fact, most modern home appliances have dozens of relays. However, in many different types of appliances and systems, one relay will not be enough to accomplish the end goal. That is when power relays come into play.
How Does a Relay Work?
In order for a relay to operate, it needs three basic components: a coil of wire, a switch that can open a circuit, and a set of contacts.
When the relay is not being used, electricity flows through the coil of wire and then back to the battery. The key component of a relay is the switch which can interrupt this flow of electricity. It does this by opening up some contacts which breaks the circuit.
In turn, when these contacts are open, it prevents current from flowing through the coil of light. In addition to this function, there are other types of relays that have many different functions such as temperature regulating or shock protection for sensitive equipment.
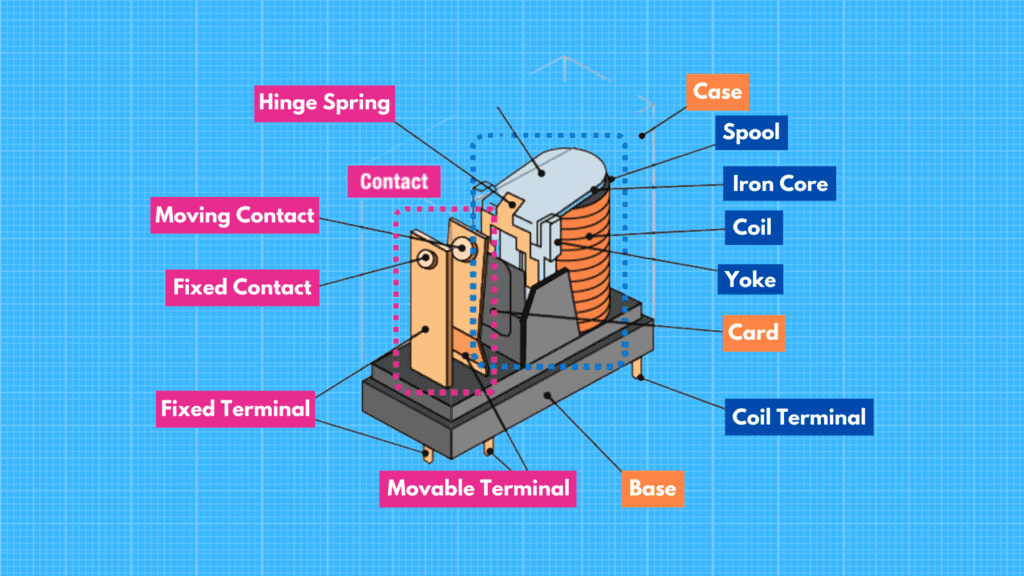
We hope you now understand what is a relay.
Normally Open and Normally Closed Relays
Normally open relays are switches that are opened by default. This means that the electrical current will flow through the switch when it is in the open position.
Normally closed relays, on the other hand, are switches that are closed by default. This means that the electrical current will not flow through the switch when it is in the open position.
How to wire a relay?
When wiring a relay, the most important thing to keep in mind is that the relay must be controlled by a switch that can handle the current that the relay will be drawing. In addition, you must have a way of grounding the relay.
The easiest way to do this is to connect the ground wire from the relay to a ground screw on the chassis.
Finally, you must make sure that the voltage rating of the relay is greater than or equal to the voltage rating of the circuit.
Explore more ways you can use the relay.
Relays Types
- Electromagnetic Relays
- Latching Relays
- Electronic Relays
- Non-Latching Relays
- Reed Relays
- High-Voltage Relays
- Small Signal Relays
- Time Delay Relays
- Multi-Dimensional Relays
- Thermal Relays
- Differential Relays
- Distance Relays
- Automotive Relays
- Frequency Relays
- Polarized Relays
- Rotary Relays
- Sequence Relays
- Moving Coil Relays
- Buchholz Relays
- Safety Relays
- Supervision relays
- Ground Fault Relays
Electromagnetic Relays
Electromagnetic relays are used in a variety of applications. They are often found in home appliances such as refrigerators, microwaves, and toasters. In these cases, it is common for one relay to control many functions of the appliance. I
n other types of products, such as vehicles or industrial machines, several relays work together to accomplish a goal. Electromagnetic relays are a very common type of relay that is used in a wide array of products.
Latching Relays
In a latching relay, the switch to control the circuit is located inside the relay. When the relay is not being used, it is closed and electricity flows through the coil of wire and then back to the battery which closes a circuit.
However, when the relay is being used to interrupt a circuit, it opens up some contacts which breaks this circuit. As mentioned earlier, these contacts are controlled by a switch that is located inside of the relay.
In order for the latching relay to operate properly, there needs to be a way for it’s current flow to function from both directions. This allows it to open and close as needed.
Electronic Relays
An electronic relay can be seen as an update on traditional electromagnetic relays. The advantage of an electronic relay is that it can be controlled via a remote signal, which means only one switch has to be located within the appliance. This allows for any external controls to control the device regardless of where it is placed.
While these are more costly than traditional relays, they are much easier to wire and make testing much easier. This is because it only requires one switch to be used instead of two or more, which can make wiring difficult on certain devices.
Non-Latching Relays
Non-latching relays are very similar to latching ones in that they both need a coil of wire, a circuit switch, and contacts for opening the circuit. However, instead of the contacts staying open, they close as soon as the electricity switches off.
These types of relays are often found in applications where a circuit needs to be completed and then removed immediately after completing this task. This is why these relays are often used in car alarms and car remotes to allow them to work even without batteries because there is no need to maintain an open circuit.
Reed Relays
A reed relay is similar to an electromagnetic relay in that it has a coil, contacts, and a magnet which act as the switch to open or close the circuit.
However, instead of this magnet being located in the center of the device like traditional relays, it is located on one end of it. In order to complete the circuit, you simply need to bring the two ends of the reed relay together which causes the magnet to touch and close the circuit. This works similarly to a switch in that as soon as contact is lost, so is the current flow and therefore completing the circuit.
High-Voltage Relays
A high-voltage relay is a type of relay that is capable of handling higher voltages.
Generally, this type of relay will have extra insulation throughout the device which helps to protect it from unexpected shocks. This also means that these relays are only suitable for use in HV circuits. Be sure to look for a HV rating on the product before considering purchasing a relay.
Small Signal Relays
Small signal relays are often used in the medical industry to help regulate the flow of voltage. These relay switches are able to handle much lower voltages than HV relays, which makes them safer for use in sensitive equipment.
The only downside is that these small signal relay switches are quite large and bulky, so they cannot be used in compact small devices like cell phones.
Time Delay Relays
Time delay relays are similar to the on/off time delay switches in that they use a small amount of current to hold open a circuit for a short period of time.
This makes them ideal for applications where an appliance would need to be turned off at night or during other times when it is not needed.
Multi-Dimensional Relays
A multi-dimensional relay is a type of relay that has 3 or more contacts and can therefore carry out a number of functions.
This type of relay is advantageous because it only requires one switch to work for multiple functions, which saves space and wiring. It also means that the parts are often less expensive than those found in traditional relays.
Thermal Relays
Thermal relays are known as self-regulating and therefore require no external power source. This design offers a low cost and reliable method, which can be used for industrial or commercial applications.
The only downside is that thermal relays are bulky and therefore not suitable for use in small circuits.
Differential Relays
Differential relays are an interesting type of relay that has two contacts on one side for HV circuits and two contacts on the opposite side for LV.
This is advantageous because it can provide a significant cost savings to manufacturers because they only need to produce one relay instead of two.
The trade-off is that this design does not work well with many circuits which contain both HV and LV components.

Distance Relays
Distance relays are a unique type of relay that is able to transmit signals from one point to another. The distance between the two points is the only limit when it comes to these types of signals, which makes it ideal for use in long-distance applications.
A specific advantage of this type of relay is that it does not require a power supply and can therefore be used in remote areas. This makes it a practical option for many commercial and industrial applications.

Automotive Relays
Automotive relays are most commonly used in cars to power on or off certain parts of the engine which are controlled by an internal computer. This type of relay is most effective when it is protecting circuits from voltage spikes because it doesn’t require any extra power to operate.
The downside is that automotive relays are designed with specific needs in mind and cannot be used for low or high-voltage applications.
Frequency Relays
Frequency relays are unique because they use a device known as a quartz crystal.
When the voltage is applied to the circuit, the crystal will vibrate at the same frequency as the input. This allows for accurate and fast switching between two different voltages which can be very advantageous for some applications.
These types of relays are relatively new on the market and not yet widely used in large-scale industry, so it is important to look into them before making a decision to purchase one.
Polarized Relays
Polarized relays are a unique type of relay that is able to manage alternating current and direct current. The design separates the switching contacts into two sections, which can be used independently from one another to make a circuit work with DC electricity.
This type of relay works well because it only has to deal with one type of voltage but may not be as practical as other types for use in certain circuits.
Rotary Relays
A rotary relay is a type of relay that is designed to use alternating current, but can also work with direct current as well. The separate contacts on the contactor are required to be connected in order to make this work.
It’s advantageous because it only has to deal with one type of voltage, which helps simplify the process of using it for certain applications.

Sequence Relays
Sequence relays are a type of relay that is able to take a number of inputs and sequence them in the order that they were put into the circuit.
The design becomes advantageous when it is being used for industrial applications because it does not require any external power supply to operate. It can also be arranged in a variety of different combinations, which means that there is usually one available for every application.
The disadvantage is that these types of relays are not well-suited for high or low voltage applications because they only have one set of contacts which limits their usefulness.

Moving Coil Relays
Moving coil relays are a type of relay that is able to switch between two different voltage levels, and they do so in a very fast manner.
This relay is often used because it only requires one set of contacts to be switched in order for the circuit to work.
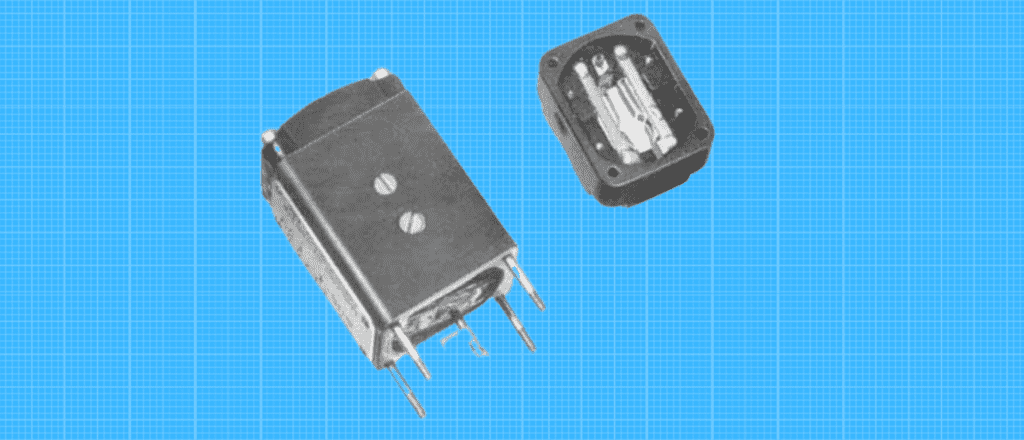
Buchholz Relays
A Buchholz relay is an electrical switching device which supports alternating current. It works by interrupting the current in one coil when the voltage in the other coil reaches a certain level.
The entire relay is enclosed in an airtight case to protect against corrosion and dust particles.
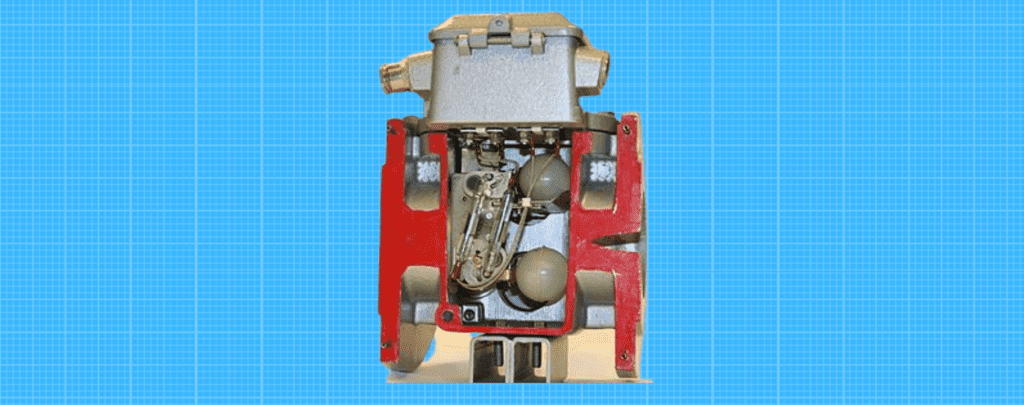
Safety Relays
Safety relays are a type of relay that is designed to interrupt the current when a certain level is reached. One advantage of using safety relays is that they are very efficient in terms of power consumption.
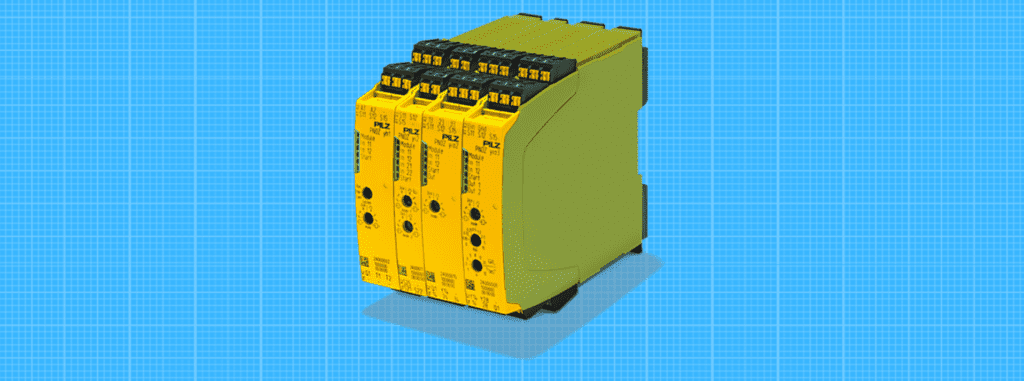
Supervision relays
The relay supervisor is a relay that is designed to supervise the other relays in a circuit. They are often used when the circuit is made up of many different types of relays for industrial or commercial purposes.
The advantage of having this type of relay is that it will prevent communication errors with the different types of relays in the circuit.
This type of relay can also help to control communication between various devices, which helps make it easier for industrial and commercial use.
One disadvantage is that they draw more power than regular industrial or commercial-grade circuits because these types of relays tend to be more complicated.

Ground Fault Relays
Ground fault relays work to detect the difference in voltage between two different parts of a circuit.
One method that they use to do this is by checking whether the current at one point in the circuit is greater than what is expected for that part of the circuit. If it is, then there may be a ground fault, which will interrupt the power to prevent electrocution from occurring.
A disadvantage of this type of relay is that they are only able to detect ground faults on a single or double-phase system and cannot detect them on a 3-phase system.
It also relies on being able to measure electricity rather than amperage, which can lead to some of its disadvantages about being unable to detect 3-phase faults.

How to control the relay?
There are a few ways to control a relay. One is to use a control switch, which is usually a toggle switch or a rocker switch. Another way to control a relay is to use contact control, which uses either a normally open or normally closed switch to control the relay. Finally, you can use switching control, which uses an electronic switching device to control the relay.
History of Relay
Joseph Henry was the person who invented the electrical relay. The first relay he created was in 1835 and it consisted of a pivoted metal point and a metal plate. The wire from the coil would come in contact with the metal point causing an electrical charge to pass through to the metal plate. The metal plate could then complete the circuit by providing power to other wires that were connected to it. This relay was very simple because it only gave off a single impulse to trigger other devices.
Joseph Henry created his first electrical relay in 1835 and afterwards he improved the design by using it in telegraphy. Along with creating this relay Henry also used his invention in experimental ways such as lighting one of his own houses with his newly created telegraph system. Henry also made the concept of the relay widely known to many people in order for them to expand on it and create their own versions of this device.
Henry’s invention was so important because without electrical relays modern life would be very different. They are used extensively in computers, both in their software and hardware, as well as in other electronic devices such as televisions and automatic garage door openers. The mechanism that Henry created was also used to create many types of relays such as magnetic (used in telephone systems), mechanical (use for alarms), and water level indicators.
Joseph Henry was a very important part in the creation of electrical relays, he created the first one and also helped many people invent new types of those devices. Without Joseph Henry modern life would be different as we know it now, causing major problems for everything from computers to alarm systems. In conclusion this man was an important figure in the history of technology who not only revolutionized the relay but also helped other people to improve this device.
Joseph Henry is credited with inventing the electrical relay in 1835 . However, according to Bryant’s book “Electricity and magnetism”, it was Joseph Henry’s assistant that actually came up with the idea of using a vibrating wire to act as an electrical switch. The assistant being Leonard Gale who worked with Henry on the idea of using the relay in telegraphy . Only one year later though did Joseph Henry create an electromagnetic device that could actually be used in telegraphy and was more efficient than what Gale had come up with.
Henry’s invention of the electrical relay was very important because it allowed for power to be transmitted over long distances. Before the device was created telegraph systems were limited to how much power they could use which caused problems when transmitting information due to the amount of energy needed. By having a device that allowed for power to be transmitted over larger areas the telegraph system was able to vastly improve allowing for more complex communication. Furthermore, Henry’s relay also allowed for telephone systems and home alarm systems making it even more important because of its widespread use in many different fields.
